This establishes a 1:1 relationship between the key and the repository, meaning one key cannot be used to sign multiple repositories and removing a repository also removes its associated key. In addition, APT now requires repositories to be signed using stronger public key algorithms. Unprivileged user namespace restrictions. APT (Advanced Package Tool), is a package managing toolkit primarily responsible for repository configuration in Ubuntu and other Debian-centric Linux distros. APT uses a list of repositories to fetch software packages and updates.In this writing, I will discuss the basics & configuration of apt repositories in-depth along with some useful practical examples using the command line.

Add a PPA Repository Linux Package Management APT YouTube
[Solved] How to install a list of packages using aptget? 9to5Answer
How to List Installed Packages in Ubuntu With APT

How to add Apt Repository in Ubuntu system Linux Tutorial Hub

APT Package Management Backup and Reinstall Packages Using APT Clone YouTube
How To List Installed Packages in Linux Using Package Management (2022)
How to Use APT Package Manager in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Its Linux FOSS

How to list installed packages with apt command on Linux Linux Tutorials Learn Linux

How to list and remove PPA repository on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux Linux Tutorials Learn Linux
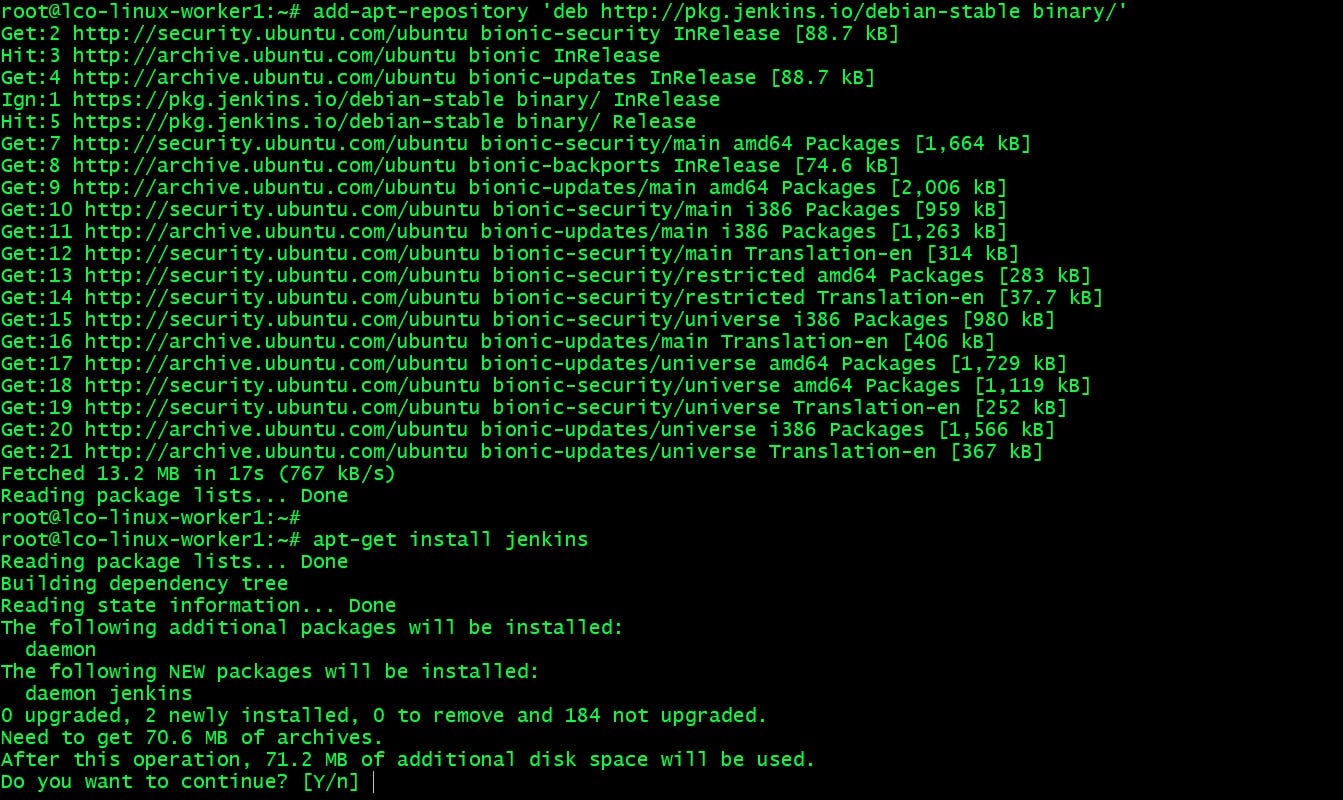
Repository and Package Management on Linux
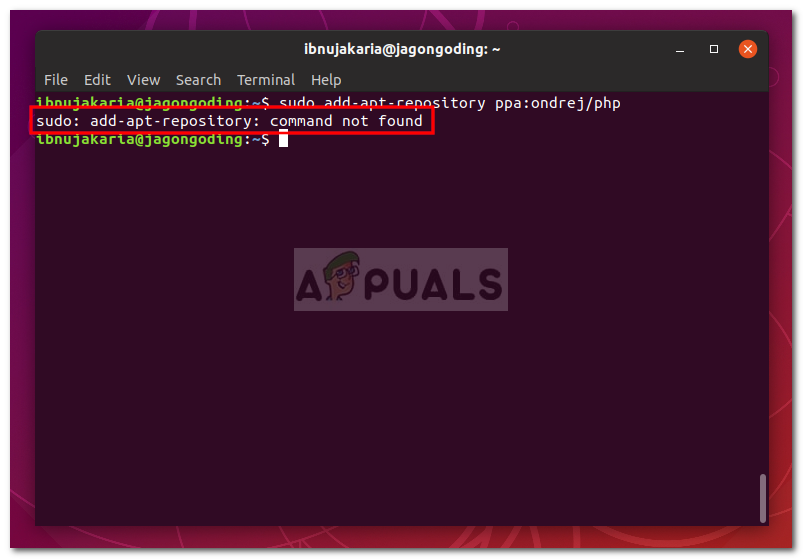
How to Fix ‘Addaptrepository’ Command not Found
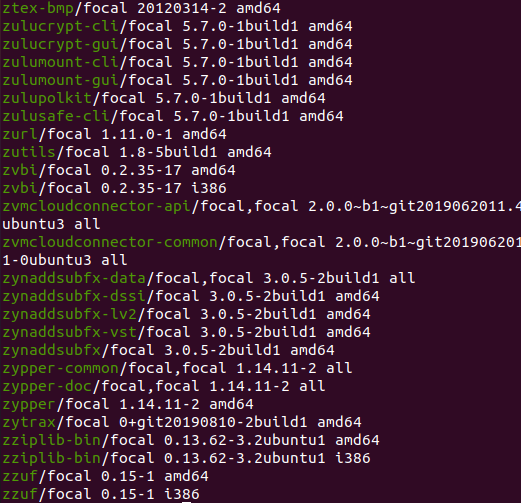
Apt List Installed Packages

How to list the packages installed in Ubuntu with APT

Ubuntu Pinning package using own repository and aptget YouTube

How to update packages shown in sudo apt update and apt list upgradable in linux? YouTube
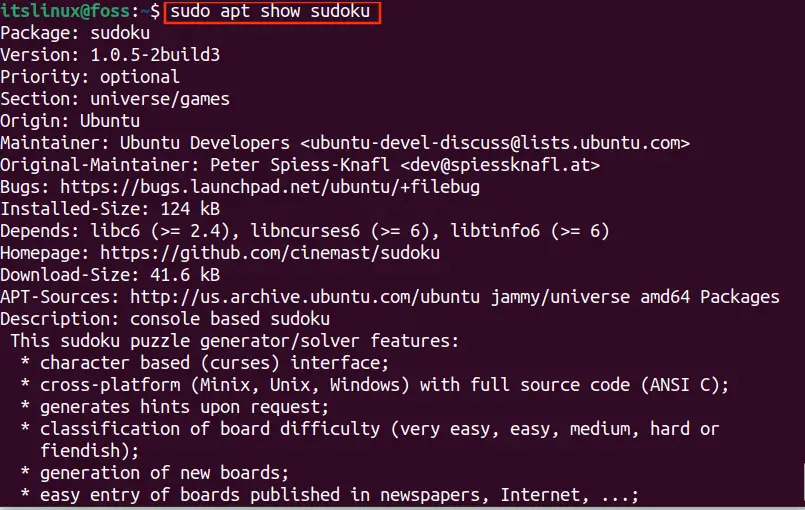
How to Use APT Package Manager in Ubuntu 22.04 LTS Its Linux FOSS
Understanding and Using sources.list for Ubuntu
List Upgradable Packages With apt Command in Ubuntu

APT Package Manager on Linux Explained devconnected Linux, Linux operating system, Management

How To List All Packages In A Repository On Ubuntu, Debian Or Linux Mint [APT] Linux Uprising Blog
sudo apt-get update. Now, navigate to /var/lib/apt/lists directory. Then search for the file with the repository name, path and architecture, ends with _Packages in there name. See the content of *_Packages to view details about all packages available under that repository. To list the packages only available in file, execute below like:. Step 3: Refresh Package List. Before proceeding with the installation, you should update the package list. Run the below command to update the APT repositories index. sudo apt update Code language: Bash (bash) Update package list. As you can see, your new Google Chrome repository is now available and ready to be used.